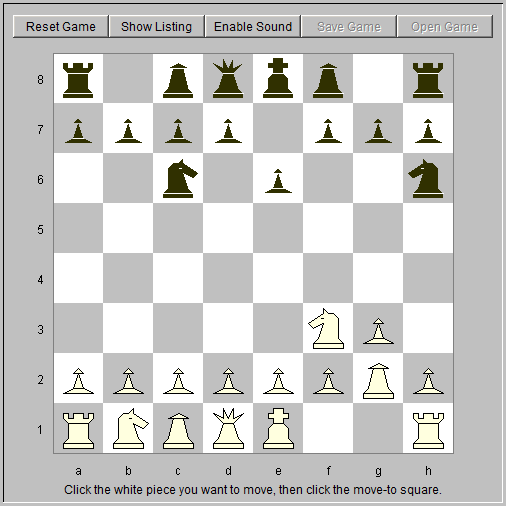
Fig. 1: Position after 3. ... Nh6.
Rick Wagner versus Homeostatic Chess Player on an Intel Core i7, minimum search depth = 6 Double fianchetto opening White Black 1. Nf3 e6 2. g3 Nc6 3. Bg2 Nh6 This knight move is not usual for humans but characteristic for this computer chess player (fig. 1).

4. O-O Be7 5. b3 O-O 6. Bb2 f5 The point of the earlier knight move: keeping his lines open (fig. 2).
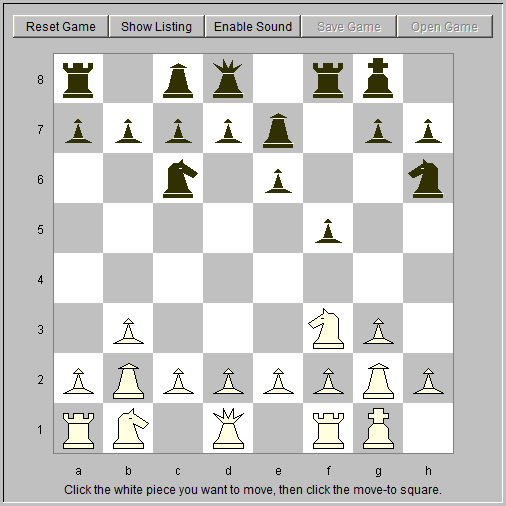
7. c4 Rb8 8. Nc3 b6 9. d4 Bb7 Black fianchettos his queen's bishop (fig. 3).
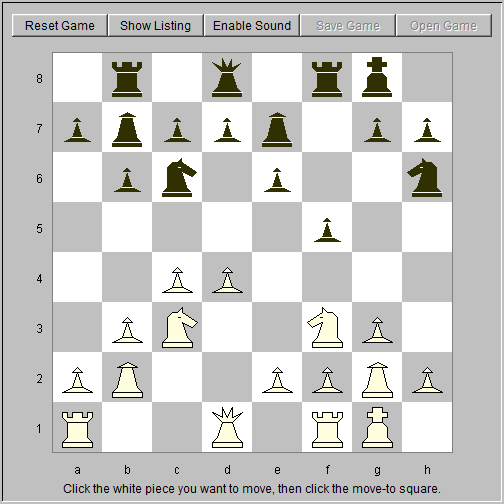
10. Re1 Na5 White prepares a pawn advance. 11. e4 fxe4 12. Nxe4 d5 Black blocks in white's queen bishop behind the white queen pawn (fig. 4).
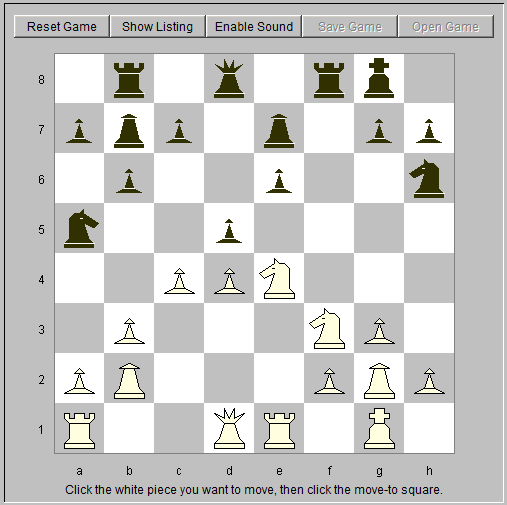
13. cxd5 exd5 14. Nc3 Kh8 15. Ne5 c6 16. Bh3 Bc8 Contesting the diagonal (fig. 5).
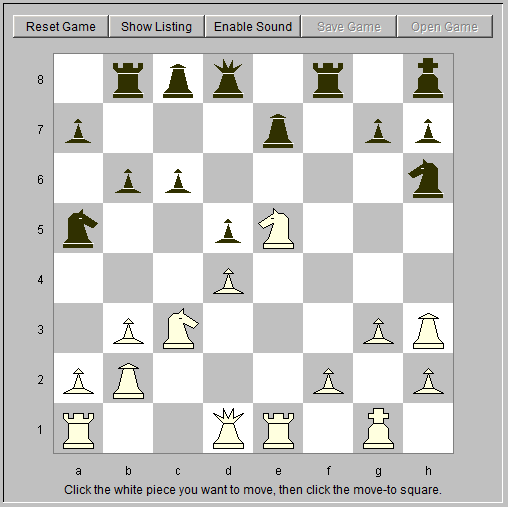
17. Qh5! Bd6 18. Re3 b5 19. Ra1e1 b4 White occupies the open file. 20. Na4 Bxh3 21. Qxh3 Qc8 Black is now desperate to neutralize white's attack (fig. 6).
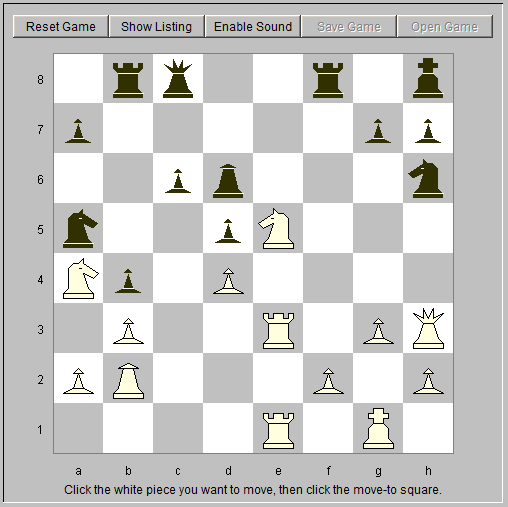
22. Qh5! Rb5? ... Rf5 might have been better. 23. Nc5 Nb7 White offers the sacrifice of a pawn to get an open diagonal for the queen's bishop but black declines. 24. Ne5d7 Rg8 White's attack is now irresistable (fig. 7).
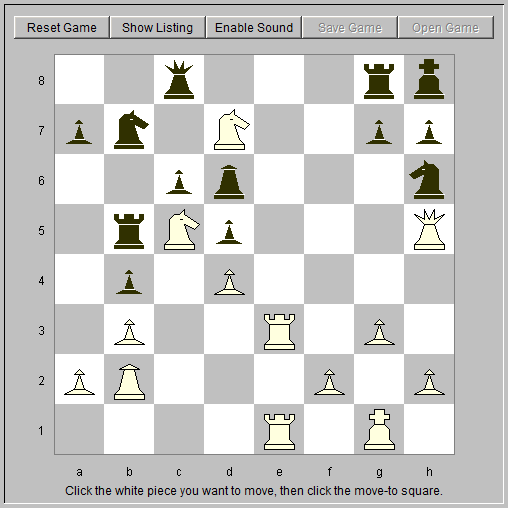
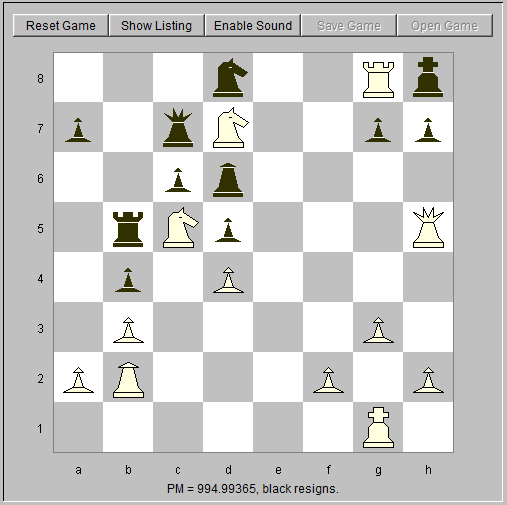
25. Re8 Qc7 26. Rxg8+ Nxg8 27. Re8 Nd8 28. Rxg8+ Black resigns. Mate is coming.
For stronger play, the computer can be held to a particular search depth with control-I to increment the look-ahead depth. Turn on the Java console to see search depth. Control-V turns on verbose mode for more information in the console.
To use the chess player applet to view these games, put it into human-human mode with control-H. Then move the pieces for both sides in accordance with the listings below.
Computer vs Rick December 19, 2012 Computer is white White Black 1. e4 e5 2. Qh5 Nc6 3. Bc4 g6 4. Qf3 Nf6 5. Ne2 Bg7 6. Nb1c3 O-O 7. O-O d6 8. h3 Be6 9. Nd5 Na5 10. Nxf6+ Bxf6 11. Bxe6 fxe6 12. b4 Nc6 13. b5 Nd4 14. Nxd4 exd4 15. Bb2 e5 16. Qb3+ Kg7 17. f4 Qd7 18. fxe5 dxe5 19. Ba3 Be7 20. Rxf8 Rxf8 21. Bxe7 Qxe7 22. Qd5 Qf6 23. Qxb7 Qf2+ 24. Kh1 Qxd2 25. Qxc7+ Kh6 26. Qxa7 Qxc2 27. Qe7 Rf2 28. b6 Rxg2 29. b7 Qb2 30. Qh4+ Kg7 31. Qe7+ Kh6 32. Qf8+ Kg5 33. Qd8+ Kh6 34. Qf8+ Kg5 35. Qe7+ Kh6 Draw Computer is white White Black 1. e3 e5 2. Nc3 Nf6 3. Bd3 d5 4. f4 Bg4 5. Be2 Bxe2 6. Ng1xe2 Nb8d7 7. O-O c6 8. b3 Bd6 9. Ng3 O-O 10. Nf5 Bc7 11. Ba3 Re8 12. Nd6 Bxd6 13. Bxd6 exf4 14. Rxf4 Ne5 15. Ba3 Qc7 16. Rb1 Ng6 17. Rd4 Re5 18. Qf1 Rh5 19. g3 Re8 20. Ra4 b6 21. Kg2 a5 22. h4 Qd7 23. Qa6 Qf5 24. Qxb6 Qxc2 25. Rb2 Qf5 26. Rxa5 Ne5 27. Bd6 Qf3+ 28. Kh2 Nf6g4+ 29. Kg1 Qf2+ White resigns Computer is white White Black 1. Nc3 d5 2. d4 Nf6 3. Qd3 a6 4. e4 c5 5. Nxd5 Nxd5 6. exd5 Qxd5 7. dxc5 Qxc5 8. Be3 Qa5+ 9. Qd2 Qxd2+ 10. Kxd2 Nc6 11. Bd3 e5 12. c3 Be6 13. Bb6 Be7 14. h4 White equalizes in 14 moves. Computer is white. June 29, 2013. Computer held to search depth of six minimum. White Black 1. Nh3 c5 What looks like a beginner's opening move on white's part has some potential. 2. e4 Nc6 3. Bc4 e6 4. d3 d5 5. exd5 exd5 6. Qe2+ Be7 7. Bb5 a6 8. Bxc6+ bxc6 9. O-O Nf6 10. Nc3 O-O White has developed consistently. If black plays Qc7 then the knight at h3 allows Bf4. 11. Ng5 h6 White's first error, allowing black's Qc7. 12. Nf3 Qc7 13. Rb1 Bg4 White is wandering. Needed is bishop development. 14. h3 Bh5 15. g4 Bg6 Another white mistake, exposing the king. 16. Ne5 Bh7 17. g5 hxg5 18. Bxg5 Bd6 White finally gets his bishop out. 19. Ng4 Nxg4 20. Qxg4 Ra8e8 Black takes control of the open file. 21. Bd2 Re6 Bh6 would give white the initiative. 22. Kh1 f5 23. Qa4 Qc8 24. Rb1e1 Rf8f6 25. Bf4 d4 26. Bxd6 Rxd6 27. Qc4+ Kh8 28. Na4 f4 29. Kg1 Rh6 30. f3 Rxh3 31. Re2 Rg3+ 32. Kf2 Rd5 33. Nb6 Qh3 34. Re8+ Bg8 35. Ke1 Qh5 36. Rxg8+ Kxg8 37. Nxd5 cxd5 38. Qxc5 Rxf3 39. Qc8+ Kh7 40. Rxf3 Qxf3 41. Qxa6 Qe3+ 42. Kf1 f3 43. Qe6 Qxe6 44. Kf2 Qe3+ 45. Kg3 f2+ 46. Kg2 Qe2 47. c4 f1=Q+ White resigns Computer white, human black, forced level 6. March 17, 2014. Queen pawn opening. White Black 1. d4 Nf6 2. Qd3 d5 3. Bf4 e6 4. Nc3 a6 5. Nf3 c5 6. Qd2 Nc6 7. dxc5 Bxc5 8. e3 O-O 9. Be2 Bb4 10. Bd3 Ba5 11. a3 b5 12. b4 Bb6 13. O-O-O Bb7 14. Qe2 Qe7 15. Ne5 Rf8c8 16. Na2 h6 17. Rh1g1 a5 18. Bxb5 axb4 19. Bxc6 Bxc6 20. Nxc6 Rxc6 21. Nxb4 Rc4 22. Bd6 Qa7 23. Rd3 Ne4 24. Be5 f6 25. Bd4 Bxd4 26. Nxd5 exd5 27. exd4 Rxd4 28. Rg1d1 Rxd3 29. Rxd3 Qc5 30. Qe3 Rc8 31. Qxc5 Rxc5 32. f4 f5 33. Rb3 Ra5 34. Rb8+ Kf7 35. Rb7+ Kg6 36. Rb6+ Kh5 37. Rb7 g6 38. Rb3 g5 39. Rh3+ Kg6 40. fxg5 hxg5 41. Rb3 Kf6 42. Rb6+ Ke5 43. Rb3 Nd6 44. Re3+ Kf6 45. Rd3 Nc4 46. Rb3 Rxa3 47. Rxa3 Nxa3 48. Kb2 Nc4+ 49. Kc3 Ke5 50. Kd3 Kf4 51. Kd4 Ne3 52. g3+ Kf3 53. c3 f4 54. gxf4 gxf4 55. Ke5 Kg4 56. h3+ Kg3 57. Kd4 Kxh3 58. c4 dxc4 59. Ke4 Kg3 60. Kd4 Kf3 61. Kc3 Ke2 62. Kb4 f3 63. Kc3 White's game is lost Computer is white, Rick is black, level 6 enforced, March 1 and 2, 2014. White Black 1. e3 c5 2. Nc3 Nc6 3. Bc4 Nf6 4. Nf3 d5 5. Bb5 Qc7 6. O-O a6 7. Bxc6+ bxc6 8. b3 e6 9. Bb2 Bd6 10. Rb1 O-O 11. h4 e5 12. Ng5 h6 13. Nf3 Bg4 14. Qc1 e4 15. Ne1 Bh5 16. d3 Rf8e8 17. Qd2 Ng4 18. g3 Re6 19. Na4 Ra8e8 20. Qc3 Rg6 21. Nxc5 Nxe3 22. fxe3 Bxg3 23. Kh1 Qc8 24. Ne6 Qxe6 25. Rf5 Qxf5 26. Ng2 Qh3+ White resigns
Rick vs. computer, July 2013, minimum depth of 6 tempi. Initial depth 8 tempi. Nimzovitch Defense. Black gets a pawn up and wins in the endgame. 1. e4 Nc6 2. d4 d5 3. exd5 Qxd5 4. Nf3 Bf5 5. Nc3 Qd6 6. a3 Nf6 7. Bb5 a6 8. Ba4 b5 9. Bb3 Na5 10. Ba2 Rd8 11. h3 Rg8 12. O-O Rh8 13. Be3 Be6 14. Bxe6 fxe6 15. Qe2 Nc6 16. Ra1d1 Rb8 17. Rd3 b4 18. Nb1 bxa3 19. Nxa3 Qd5 20. c4 Qe4 21. Ng5 Rxb2 22. Qxb2 Qxd3 23. Nxe6 h5 24. Nxc7+ Kf7 25. d5 Nd8 26. Qa2 a5 27. Rb1 Ne8 28. Na3b5 Nxc7 29. Nxc7 g6 30. c5 Bg7 31. Rb8 Qd1+ 32. Kh2 Qa1 33. Qc4 Be5+ 34. Bf4 Qd4 35. Qxd4 Bxd4 36. Ne6 Nxe6 37. dxe6+ Kxe6 38. Rxh8 Bxh8 39. c6 Bd4 40. Kg3 Bb6 41. Kf3 a4 42. Bc1 Kd5 43. Ba3 e6 44. Ke2 Kxc6 45. f3 Bc7 46. Kd3 Kb5 47. Be7 Be5 48. Ba3 Ba1 49. Bd6 Bb2 50. Be7 a3 51. Kc2 Kc4 52. White resigns Computer is black White Black 1. d4 e6 2. e4 Qh4 3. Bd3 Nc6 4. Nf3 Qg4 5. O-O Nb4 6. Nc3 Nxd3 7. Qxd3 Be7 8. h3 Qh5 9. Ne2 Qa5 10. Bd2 Bb4 11. c3 Be7 12. a3 Qb6 13. b4 Nf6 14. d5 White has an advantage in space and development. Computer is black White Black 1. f4 Nc6 2. Nf3 d6 3. g3 Nf6 4. Bg2 Bf5 5. O-O e6 6. d3 d5 7. h3 Bc5+ 8. Kh2 h6 9. c3 O-O 10. a4 Kh8 11. b4 Bd6 12. Nb1d2 Rb8 13. Bb2 Qd7 14. Qb3 Bh7 15. Ra1e1 a6 16. e4 dxe4 17. dxe4 Be7 18. Nd4 Nh5 19. g4 Nf6 20. b5 Na5 21. Qa2 c5 22. c6 Nxc6 23. e5 Ne8 24. Ba3 Nxd4 25. Bxe7 Computer is black White Black 1. e4 Nc6 2. Nf3 Nf6 3. e5 Ng4 4. d4 e6 5. h3 Nh6 6. Bc4 d5 7. d6 Bxd6 8. O-O Na5 9. Bd3 Be7 10. Bd2 Nc6 11. Re1 Ng8 12. c3 Kf8 13. Qc2 Computer is black White Black 1. Nf3 Nc6 2. e4 e6 3. d4 Nf6 4. Nc3 Bb4 5. Bd3 d5 6. Bg5 Qd7 7. O-O Bxc3 8. Bxf6 gxf6 9. bxc3 O-O 10. h4 dxe4 11. Bxe4 f5 12. Bd3 Qd5 13. h5 Bd7 14. h6 Kh8 15. c4 Qd6 16. Rb1 Ra8b8 17. c3 Rg8 18. Bc2 Qa3 Computer is black White Black 1. f4 e6 2. Nf3 Nh6 3. g3 Nc6 4. Bg2 d5 5. O-O Bd7 6. b3 Bb4 7. Bb2 O-O 8. a3 Bc5+ 9. d4 Bd6 10. c4 Ng4 11. Qd3 dxc4 12. bxc4 f6 13. h3 Nh6 14. e4 Be8 15. Nb1d2 Rc8 Computer is black June 23, 2013 White Black 1. e4 d5 2. exd5 Qxd5 3. Nc3 Qd6 4. Nf3 Bg4 5. Be2 Nf6 6. d4 Nb8d7 7. Be3 Nd5 8. Nxd5 Qxd5 9. O-O e6 10. c4 Qa5 11. a3 O-O-O 12. b4 Qh5 13. Qa4 Kb8 14. h3 Bf5 15. Rf1e1 Nb6 16. Qb3 f6 17. Ne5 Qe8 18. g4 fxe5 19. gxf5 exf5 20. dxe5 Qxe5 21. Bf3 Qf6 22. c5 Nc8 23. Ra1d1 Be7 24. Bf4 Rxd1 25. Rxd1 g5 26. Qd5 Qc6 27. Qd3 Qf6 28. Bxc7+ Kxc7 29. Qd7+ Black resigns Computer is black, June 23, 2013 White speculative rook sacrifice White Black 1. e4 d5 2. exd5 Qxd5 3. Nf3 Qe4+ 4. Be2 Bf5 5. d3 Qg4 6. O-O Nf6 7. h3 Qb4 8. Nc3 Nc6 9. Be3 Qxb2 10. Qd2 O-O-O 11. a4 Nd5 12. Nxd5 Rxd5 13. Rf1b1 Qf6 14. a5 Rg8 15. Ra2 g6 16. Ra2b2 Nxa5 17. Rxb7 Nxb7 18. Bxa7 Bd7 19. d4 Bg7 20. Qb4 Qc6 21. c3 Bf5 22. Rb2 Ra5 23. Bc5 Ra1+ 24. Kh2 Ra4 25. Qb3 Be6 26. c4 Bf8 27. Ne5 Qa6 28. Bf3 c6 29. Bxc6 Qxc6 30. Nxc6 Nxc5 31. dxc5 Rb4 32. Qxb4 Kd7 33. Ne5+ Kd8 34. Qa5+ Kc8 35. Qa8+ Black resigns Computer is black June 24, 2013 Opening pawn sacrifice and a later speculative Knight sacrifice White Black 1. Nf3 e6 2. c4 Nc6 3. Nc3 Nf6 4. g3 Rb8 5. Bg2 Bb4 6. a3 Bd6 7. O-O Ng4 8. h3 Ng4e5 9. d4 Nxc4 10. b3 Nb6 11. e4 O-O 12. Bb2 Re8 13. Qd3 g6 14. e5 Bf8 15. Ne4 Nd5 16. Nf3g5 h6 17. Nf3 b5 18. Nh4 b4 19. a4 g5 20. Nf3 Na5 21. Bc1 d6 22. Nf3xg5 dxe5 23. dxe5 hxg5 24. Nxg5 f5 25. f6 Nxf6 26. Qg6+ Bg7 27. Bb2 e5 28. Nf7 Qe7 29. Nxe5 Bb7 30. Rf1e1 Qf8 31. Bxb7 Rxb7 32. Ra1d1 Nxb3 33. Nc6 Rxe1+ 34. Rxe1 Qd6 35. Ne7+ Kf8 36. Nf5 Qd7 37. Re7 Qd1+ 38. Kh2 Ng4+ 39. hxg4 Qh1+ 40. Kxh1 Black resigns Computer is black, June 26, 2013 Draw by repetition. Black obtains the bishop pair and nullifies white's lead in development. White Black 1. e4 e6 2. d4 Qh4 3. Nc3 Bb4 4. Bd3 Nf6 5. Nf3 Qg4 6. Qe2 Nh5 7. O-O Nf4 8. Bxf4 Qxf4 9. a3 Be7 10. Rf1e1 O-O 11. Ra1d1 a5 12. e5 b6 13. d5 Bb7 14. Be4 Ba6 15. Bd3 Bb7 16. Be4 Ba6 17. Bd3 Bb7 Draw Computer is black, February 22, 2014 Black wins a pawn in the opening and carries it through to a winning endgame. White Black 1. e3 e5 2. Nc3 d5 3. Qh5 Nc6 4. Bb5 Qd6 5. Nf3 Nf6 6. Qxe5+ Qxe5 7. Nxe5 Bd7 8. Nxd7 Kxd7 9. Ke2 a6 10. Bd3 g6 11. Kd1 Ne5 12. Be2 c6 13. Na4 Re8 14. Rb1 Ne5g4 15. Ke1 b5 16. Nc3 Bc5 17. f3 Nh6 18. b4 Ba7 19. Kf2 d4 20. Nd1 dxe3+ 21. dxe3 Nf5 22. Bb2 Re6 23. Rf1 Rh8e8 24. Bd3 Nxe3 25. Nxe3 Nd5 26. Kg3 Nxe3 27. Rf1c1 Bb8+ 28. Kh3 f5 29. Rh1 Nd5 30. Bc1 Nc3 31. Rb2 Re1 32. Rxe1 Rxe1 33. Bd2 Rh1 34. g3 Nd5 35. c4 Nb6 36. cxb5 c6xb5 37. Rc2 Nd5 38. Rc5 Kd6 39. Rc8 Bc7 40. Ra8 Rd1 41. Rxa6+ Ke5 42. Bh6 Nxb4 43. Be2 Nxa6 44. Bxd1 Kd4 45. Bb3 Nb4 46. Bg8 Kc3 47. Bxh7 Nxa2 48. Bxg6 b4 49. Bxf5 b3 50. Bg7+ Kd2 51. Kg2 Nc3 52. f4 b2 53. Bxc3+ Kxc3 54. Bh7 Kd2 55. Kf3 Kc1 56. g4 b1=Q 57. Bxb1 Kxb1 58. g5 Ba5 59. f5 Bc3 60. f6 Kc2 61. Ke4 Black resigns Queen's Indian Opening White: Rick, Black Computer White Black 1. b3 e6 2. Bb2 Nc6 3. e4 Qh4 4. Nc3 Bc5 5. g3 Qh6 6. Nf3 Nf6 7. d4 Bb4 8. Qd3 O-O 9. Bg2 b6 10. O-O Bb7 11. a3 Be7 12. Rf1e1 a5 13. d5 exd5 14. exd5 Ba6 15. Qd1 Nxd5 16. Qxd5 Qd6 17. Qh5 g6 18. Qh6 g5 19. Qh5 Qg6 20. Qxg6+ f7xg6 21. Ne5 Bc5 22. Ne4 Bd4 23. Bxd4 Nxd4 24. Ra1c1 Ne2+ 25. Rxe2 Bxe2 26. Nxd7 Rf5 27. Nd6 cxd6 28. Bxa8 Bf3 29. Bxf3 Rxf3 30. Nxb6 Rc3 31. a4 Rc5 32. Nc4 d5 33. Ne3 d4 34. Nc4 Kf8 35. Rd1 Rd5 36. f3 h5 37. Kf2 h4 38. Ke2 Ke7 39. Kd3 hxg3 40. hxg3 Kf7 41. Ke4 Rc5 42. Rxd4 Rc7 43. Rd5 Re7+ 44. Re5 Ke8 45. Rxe7+ Kxe7 46. Ke5 Kf7 47. Nxa5 Ke7 48. c4 Kf7 49. b4 g4 50. fxg4 Ke7 51. Nc6+ Kd7 52. b5 g5 53. c5 Kc7 54. Kf5 Kb7 55. Kxg5 Kc7 56. Kf6 Kb7 57. g5 Ka8 58. g6 Black resigns Computer black, human white, short game, forced level 6. March 10, 2014. White Black 1. d4 e6 2. Nf3 Nf6 3. c4 Bb4+ 4. Nc3 Ne4 5. Qc2 Nxc3 6. bxc3 Be7 7. e4 O-O 8. Bd3 Na6 9. e5 h5 10. O-O d6 11. Bf4 g5 12. Be3 g4 13. Nd2 dxe5 14. dxe5 Bc5 15. Bh6 Re8 16. Ne4 Be7 17. Ra1d1 Bd7 18. Ng3 h4 19. Qe2 Kh8 20. Qe4 Black resigns Computer is black, level 6 minimum. April 8, 2014. A speculative sacrifice of the exchange by white on move 20 results in a strong attack. White Black 1. e4 d5 Center counter defense. 2. exd5 Qxd5 3. Nc3 Qe6+ 4. Be2 Bd7 5. Nf3 Nc6 6. d4 Qf5 7. a3 Nf6 White makes a phrophylactic move of the rook pawn. 8. h3 Nd5 A second phrophylactic pawn move by white. 9. O-O Nxc3 10. bxc3 Qd5 Black neglects development. 11. c4 Qd6 12. Bb2 e6 13. d5 exd5 Undoubling white's pawns. 14. cxd5 Ne7 Cramped, but other knight moves are no better. 15. c4 O-O-O 16. Be5 Qa6 17. a4 Ng6 White prevents Ba4. 18. Bg3 Qf6 Not the best diagonal for white's bishop. 19. Rb1 Bf5 White finally takes control of an open file. 20. Qb3 Bxb1 The exchange sacrifice retains white's control of 21. Rxb1 b6 the file and eliminates black's active bishop. 22. Qb5 Bd6 23. a5 Bxg3 24. Qa6+ Kb8 25. axb6 Bxf2+ Black declines the sacrifice of the bishop, but takes the pawn. 26. Kxf2 c7xb6 27. c5 Qc3 If black's rook takes the pawn, mate soon follows. 28. cxb6 Qc5+ 29. Kf1 Rd7 30. bxa7+ Ka8 Double check, the king must move. 31. Bb5 Ne7 Black prevents the bishop from checking on c6. 32. Bxd7 Qc7 33. Ne5 Rg8 This is the end. If black's queen takes the knight, it's mate at b7. 34. Nc6 Qf4+ 35. Kg1 Qe3+ 36. Kh1 Qc1+ 37. Rxc1 Nf5 38. Rb1 Ng3+ 39. Kh2 Black resigns without taking the available spite check! Inhuman. May 14, 2014. Just keeping on the pressure to punish black's premature queen sortie. Minimal look ahead of six. Computer is black. White Black 1. e4 e6 2. d4 Qh4 This premature queen sortie needs to be punished! 3. Nc3 Bb4 4. Bd3 Nf6 5. Qe2 Nc6 6. Nf3 Qh5 7. e5 Nd5 8. Bd2 Qg4 9. O-O-O Nf4 Black doesn't take the bait. 10. Qf1 Nxd3+ 11. Qxd3 Bxc3 12. bxc3 Rb8 13. h3 Qg6 14. Qe2 h5 15. Nh2 Qxg2 I need the queen to take the pawn so I can attack! 16. Nf3 Qg6 17. Rd1g1 Qh7 18. Rg2 b5 19. Rh1g1 Kf8 20. Ng5 Qg6 21. Ne4 Qf5 22. Rxg7 h4 23. Qe3 Na5 24. Nf6 Nc4 25. Rg8+ Ke7 26. Rxh8 Qxc2+ 27. Kxc2 Nxe3+ 28. Bxe3 Bb7 29. Rxb8 Be4+ 30. Kd2 Black resigns
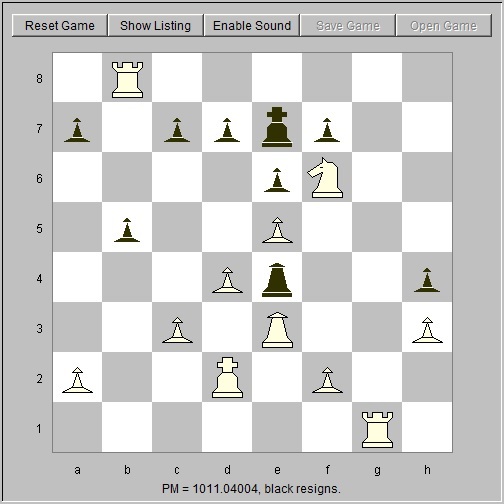
May 25, 2014, computer is black. Minimal search depth is six tempi. Black sets a trap to win a pawn. White Black 1. a3 d5 2. Nf3 Qd6 3. d4 Bf5 4. e3 Nd7 Black develops consistently. 5. c4 dxc4 Black sets a little trap. 6. Bxc4 Bxb1 7. Rxb1 Qg6 8. Bd2 Qxg2 Black gets a pawn.
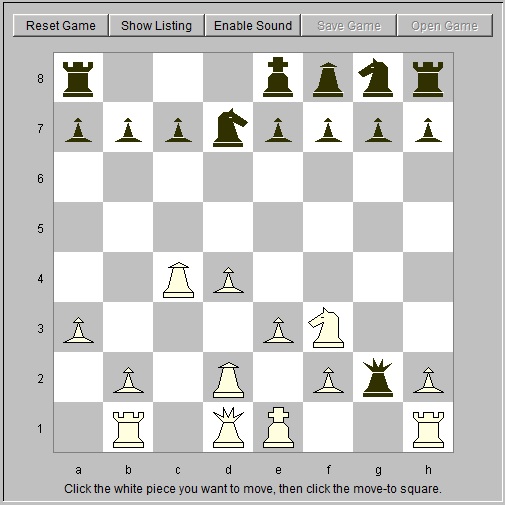
9. Rg1 Qh3 10. Ng5 Qxh2 11. Bxf7+ Kd8 Trapping the black king in the center. 12. Nf3 Qd6 White puts the knight right back. 13. Qb3 Nh6 14. Bd5 Qb6 15. Qc2 Nf6 White is a pawn down so must avoid trading queens. 16. Bc4 c5 Mistake by black. 17. dxc5 Qc7 Black realizes the mistake too late and must give back the pawn. 18. Rd1 Kc8 19. Bc3 Qc6 The pawn is still poison. 20. Be5 Nd7 Still poison because of Be6+. 21. Rxd7 Qxd7 White doesn't let off the pressure. 22. Ke2 Qc6 23. Qb3 a5 24. Rd1 Ra6 White won't let the king escape to the king side when the king hunt starts. 25. Nd4 Qg6 The pawn is still poison, but the game move isn't much better. 26. Bd5 b6 White taking the pawn also works. 27. Qc4 bxc5 28. Qxc5+ Rc6 It's all over now. 29. Nxc6 Qg4+ 30. Bf3 Qxf3+ 31. Kxf3 Black resigns
 Richard dot J dot Wagner at gmail dot com
Richard dot J dot Wagner at gmail dot com
HomeostaticGames.html, this hand crafted HTML file was created June 25, 2013.
Last updated February 19, 2019, by
Dr. Rick Wagner.
Copyright © 2013-2019 by Rick Wagner, all rights reserved.